Section 74 under the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023
Section 74 of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) criminalises any assault or use of criminal force against a woman carried out with the intention—or with the knowledge that it is likely—to outrage her modesty. The provision replaces the comparable offence once found in Section 354 of the Indian Penal Code.
Use our free tool here:
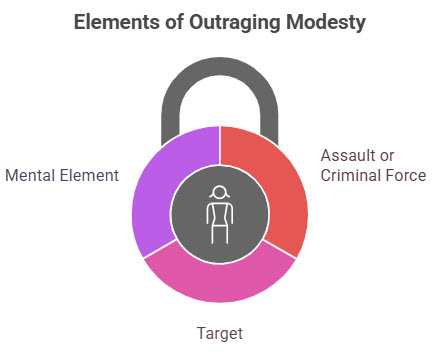
Key ingredients of the offence
-
Assault or criminal force: The act must involve a physical attack or the use of force.
-
Target: The victim must be a woman.
-
Mental element: The accused must intend to outrage her modesty or know that such an outcome is likely.
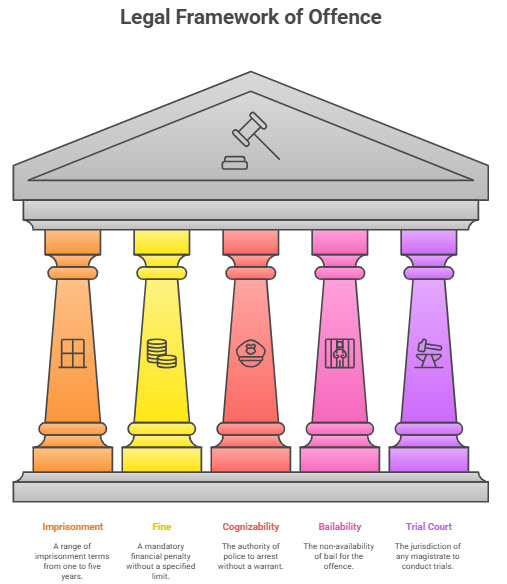
Punishment and classification
-
Imprisonment: Not less than one year, extendable to five years.
-
Fine: Mandatory, but the statute does not prescribe a ceiling.
-
Cognizability: Cognizable; police may arrest without warrant.
-
Bailability: Non-bailable.
-
Trial court: Any Magistrate.
How it differs from IPC Section 354A
Section 74 focuses on physical acts that outrage modesty. IPC § 354A, which survives in the Penal Code, covers a wider range of sexual-harassment conduct—including verbal or non-physical acts—and carries graded penalties. lawrato.com
Procedure for filing a complaint
-
Approach the jurisdictional police station and lodge a First Information Report (FIR).
-
Provide a clear account of events, names of witnesses, and any corroborative evidence (e.g., CCTV footage, messages).
-
Request a copy of the FIR; the officer in charge must supply it free of cost.
-
Seek a medical examination without delay if injuries are involved, as medical reports carry evidentiary value.
Possible defences
The accused may dispute intent or knowledge, argue mistaken identity, or challenge whether the complainant’s modesty was in fact outraged. Courts apply an objective test, considering whether a reasonable woman would feel her modesty had been violated in the circumstances.
Conclusion
Section 74 reflects the legislature’s aim to deter physical acts that insult a woman’s dignity while ensuring a minimum custodial sentence. Victims should file an FIR promptly, preserve evidence, and consult legal counsel. Accused persons should seek representation early, as the offence is non-bailable and carries a mandatory minimum term.
This article provides general legal information; it is not a substitute for individual legal advice.