Introduction:
- Employment disputes are a common occurrence in workplaces, and it is crucial to handle them legally to ensure fairness and justice.
- India, with its diverse workforce, has a robust legal framework to address employment disputes and protect the rights of both employers and employees.
- Understanding the legal mechanisms for handling employment disputes is essential for fostering a healthy work environment and sustaining industrial relations.
Legal Framework:
- The primary legal document governing employment relationships in India is the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947.
- The Act provides a comprehensive framework for the resolution of disputes and outlines the rights and obligations of both employers and employees.
- Other relevant laws include the Payment of Wages Act, 1936, the Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948, and the Minimum Wages Act, 1948.
Prevention and Conciliation:
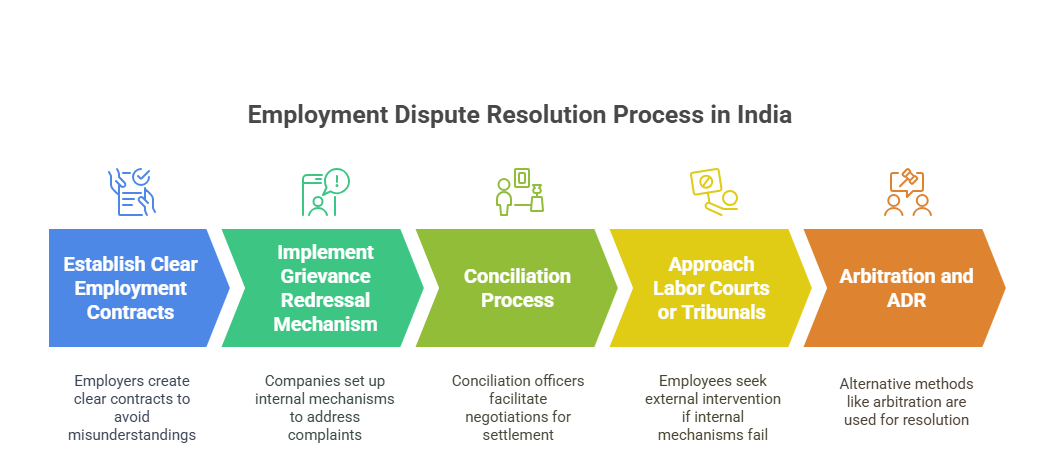
- One of the first steps in handling employment disputes is prevention. Employers can establish clear employment contracts, job descriptions, and grievance redressal mechanisms to avoid misunderstandings.
- Conciliation is a non-adversarial method for resolving disputes. The Industrial Disputes Act mandates the appointment of conciliation officers who facilitate negotiations between the parties to reach a settlement.
Grievance Redressal Mechanism:
- Companies in India are required to establish an internal grievance redressal mechanism to address employee complaints and disputes promptly.
- This mechanism ensures that disputes are resolved at the workplace level, reducing the need for external intervention.
- Employers must appoint a Grievance Redressal Officer and display the details of the grievance redressal mechanism prominently.
Labor Courts and Tribunals:
- When internal mechanisms fail to resolve disputes, employees can approach labor courts or industrial tribunals.
- These courts have the authority to adjudicate on various employment-related matters, including wrongful termination, unfair labor practices, and disputes over wages.
- The process involves filing a formal complaint, presenting evidence, and attending hearings.
Arbitration and Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR):
- Arbitration is an alternative to traditional court proceedings. It involves a neutral third party (arbitrator) who makes a binding decision after hearing both sides.
- ADR methods such as mediation and conciliation can be effective in resolving disputes without the formalities of a court or tribunal.
- Many employment contracts in India include arbitration clauses, making it a preferred method for dispute resolution.
Labor Welfare Boards:
- Some states in India have established labor welfare boards to address specific issues related to wages, working conditions, and welfare measures.
- These boards play a crucial role in promoting social dialogue and resolving disputes at a localized level.
Statutory Remedies:
- Various labor laws in India provide for specific remedies in case of unfair labor practices or violations.
- For example, if an employer fails to pay wages as per the Minimum Wages Act, an employee can file a complaint with the labor department seeking redressal.
Collective Bargaining:
- The right to collective bargaining is a fundamental right of workers in India. Trade unions play a significant role in negotiating employment terms and resolving disputes collectively.
- Employers are obligated to engage in collective bargaining in good faith, and any failure to do so can lead to legal consequences.
Judicial Intervention:
- The judiciary in India serves as the ultimate authority in resolving complex employment disputes.
- The Supreme Court and various High Courts have delivered landmark judgments clarifying legal principles and providing guidance on matters related to employment disputes.
Conclusion:
- Handling employment disputes legally in India involves a multifaceted approach, combining preventive measures, internal mechanisms, alternative dispute resolution, and, when necessary, judicial intervention.
- Employers and employees alike should be aware of their rights and responsibilities to contribute to a harmonious work environment.
- The evolving legal landscape underscores the importance of staying informed about changes in labor laws and regulations to navigate employment relationships effectively.
What is your reaction?
Excited
0
Happy
0
In Love
0
Not Sure
0
Silly
0